Perceiver review
Perceiver, General Perception with Iterative Attention, 2021
Summary
이번에 읽어본 논문은 Percevier: General Perception with Iterative Attention 입니다. Perceiver는 다양한 data modality를 다루기 위한 새로운 model architecture를 제안합니다. domain specific assumption 을 줄이기 위해 많은 고민을 한 논문이라는 생각이 듭니다. 가장 인상깊었던 부분은 image input에 대해 2D conv 같은 preprocess 없이 약 50,000 pixel에 직접적으로 attending 합니다. (conv를 사용하게 되면 locally inductive bias 를 가지게 되는데요, general model을 다루기 위한 부분에서 이런 모델의 자체적인(?) additional assumption을 최소화하기 위해 사용을 피한 것처럼 보입니다.) 모델은 기본적으로 Transformer module 을 활용한 구조로 이루어지며, asymmetric cross attention 을 통해 model complexity를 줄이고, latent Transformer 를 활용합니다. 또 explicit spatial or temporal information 을 주지 않은 데에 대해서, high-fidelity Fourier Feature를 통해 보완합니다. 결과적으로 images, point clouds, audio, video, and video+audio 등의 다양한 modality 에 대한 classification task에서 competitive 하거나 outperform 을 보여주고 있습니다.
Main Idea
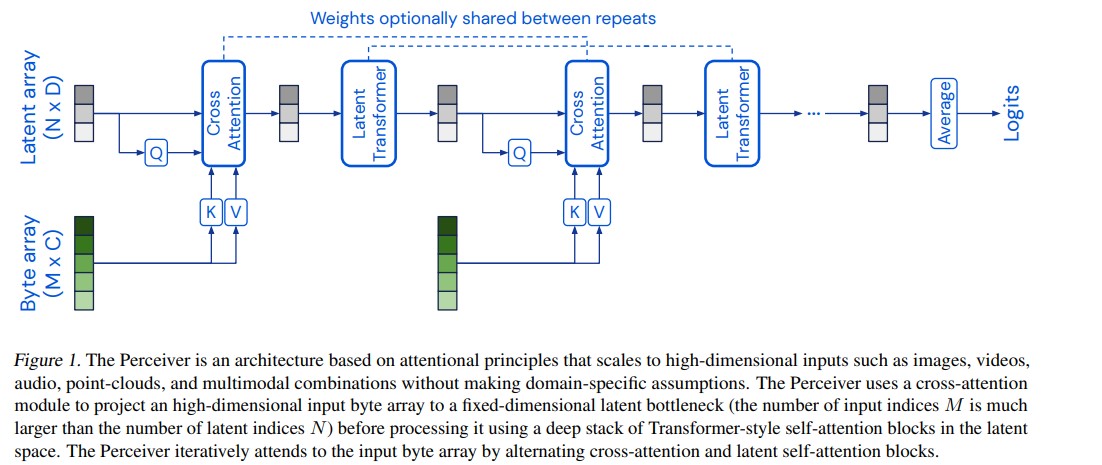
위의 그림은 Perceiver의 모델구조를 보여줍니다. Perceiver는 domain-specific assumption이 없는 high dimensional inputs을 attentional mechanism을 통해 fixed-dimentional latent bottleneck으로 scailing합니다. bottleneck이 되는 latent array 에 detail information을 매번 담기 어려운 문제가 있기 때문에 iterative하게 attending하며 그 점을 보완하고 있고, optionally weights sharing을 통해 parameter efficiency를 높여주고 있습니다. 논문에서는 이런 구조가 흡사 RNN의 format으로 해석될 수 있다고 합니다.
본 모델에서 주요할 부분은 크게 2가지 입니다. 하나는 cross-attention module이고, 다른 하나는 latent array에서 latent array 로 mapping시키는 latent transformer입니다. cross-attention module에서는 asymmetric cross attention을 사용함으로써 quaduratic scailing problem을 다소 해결하는 모습을 보여줍니다. 기존의 Transformer에서 QKV self-attention method의 단점은, input size가 매우 커지게 되면 quadratic complexity 가 매우 커진다는 것입니다. 이 때문에 image 를 pixel itself 하게 적용하지 못하는 그런 점이 있었습니다. 한편, 본 논문에서는 asymmetric cross-attention moduel을 도입하여 그 문제를 해결합니다. attention module에 사용될 K와 V를 Byte array 에서 가져오고 (MxC에서 M은 large input dimension), Q를 latent array 에서 가져오게 되는데 이 때, Q의 size는 NxD 가 됩니다. (N은 latent’s index dimension로, hyperparameter) 사이즈를 비교해보자면, N « M 로, cross-attention operation의 complexity는 $O(MN)$으로 낮아지게 됩니다.
이런 cross-attention module을 통해 input size와 상관없이 모델을 더욱 deep하게 쌓을 수 있게 됩니다.
cross-attention module에서 출력되는 차원은 latent’s index dimentsion N이므로, 입력과 비교할 때 상대적으로 작은 사이즈를 유지하게 되고, 이 때문에 latent transformer에서는 $O(N^2)$의 작은 cost만으로 연산을 이어갈 수 있습니다. input size와 상관없는 latent transformer의 self-attention operation으로 deeper한 구조 설계가 가능해졌습니다. 결과적으로 연산 complexity는 $O(MN+LN^2)$이 됩니다.
하지만 network이 bottleneck의 serverity에 의해 necessary detail information을 모두 capture하는 데에는 어려움이 있습니다. 이에 input byte array를 iterative하게 입력해 줌으로써 cross-attention 연산을 반복적으로 수행합니다. iterative 하게 입력을 해주면 그에 따라 cross-attention module + latnet Transformer block이 비례하여 증가하게 되는 것이기 때문에 compuational requirements 가 요구된다고 말하고 있습니다. (논문에서는 more cross-attention이 better performance를 낸다고 말합니다.) 한편, weight sharing을 통해 parameter efficiency를 높이는 모습도 보여주고 있습니다.
data modality에 따른 explicit한 temporal or spatial information을 주지 않고 있는데요, 모델에서는 이 부분을 Frourie Features를 입력에 함께 injection해주면서 보완하고 있습니다.
Experiments
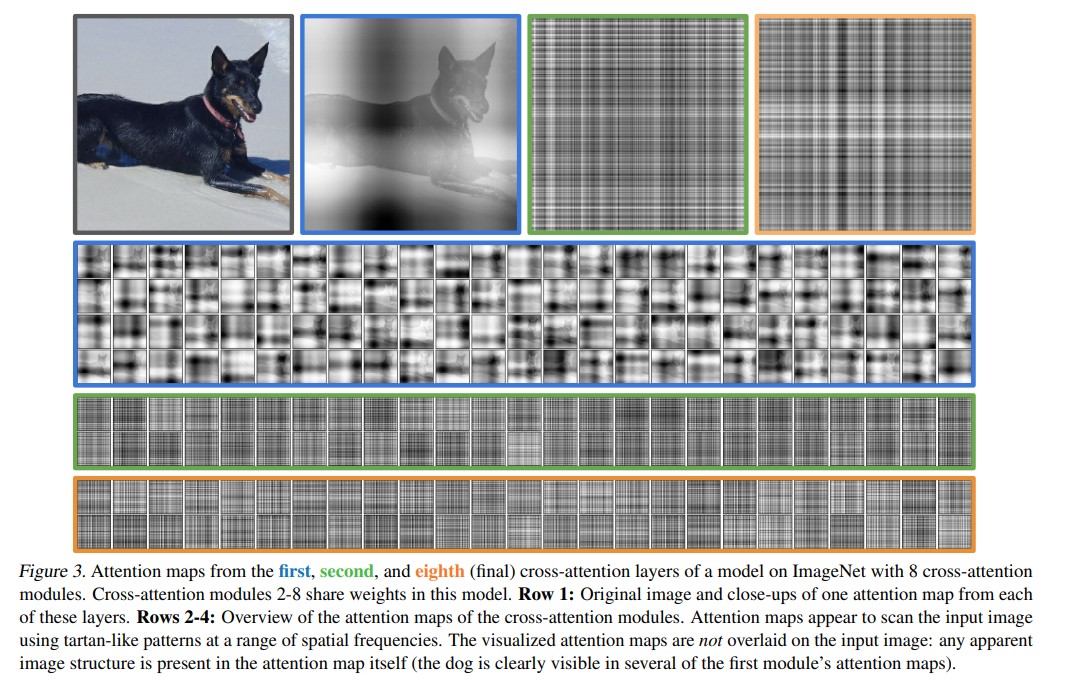
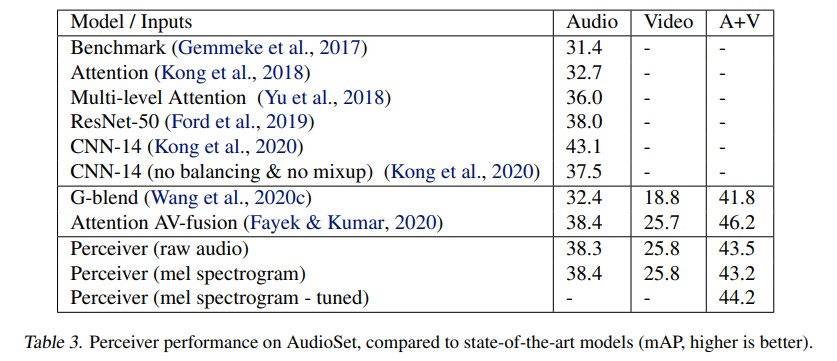
Reference
마치며
- 모델의 자체적인 captured information에 inductive bias를 최소화하기 위한 Trm기반의 general architecture가 등장했다고 생각한다. 이런 관점에서 inductive bias를 최소화하는 모델 기반의 architecture가 흥미로웠고, inductive bias를 최소화 할뿐만 아니라 조절할 수 있는 새로운 모듈이 등장할 수 있을까? 하는 생각이 든다. (진정한 generality는 숲을 볼 수도, 나무를 볼 수도 있어야 하지 않은지, 혹은 inductive bias 외의 다른 중요한 관점에서의 접근을 하는 류)
- 다양한 modality를 다루기 위해 최대한 general method를 쓰려는 방법론들이 보인 것 같다. 위에서 언급한 Trm도 그랬고, FF 또한. 기존의 position encoding에도 Fourier Feature를 사용하는 것이 흥미로웠다. (근데 최근의 연구에서는 FF를 많이 쓰는 거 같다.)
- cross-attention 을 반복적으로 수행 할수록 더 잘 된다고는 하지만, iterative input과 computational power에 limit이 없을 수 없다. bottleneck에서 오는 장점을 갖되, 더 효율적인 방법으로 그걸 보완할 수는 없을까? (detail information을 어떻게 더 잘 capture할까)
- 포스팅에 틀린 부분이 있을 수 있으니, 참고해서 봐주시면 감사하겠습니다. 오류에 대한 수정과 토론은 언제든 환영입니다! :)